- December 10, 2022
- admin
Factors to consider while designing Bulk Material Handling Design & System
Designing a bulk material handling system is no laughing matter – but that doesn’t mean it has to be a dry and boring process! In this blog post, we’ll look at the various factors you need to consider when designing your bulk material handling system, as well as some of the unique challenges you may face along the way! Let’s get started on your journey towards an efficient bulk material handling setup.
Introduction to Bulk Material Handling Systems
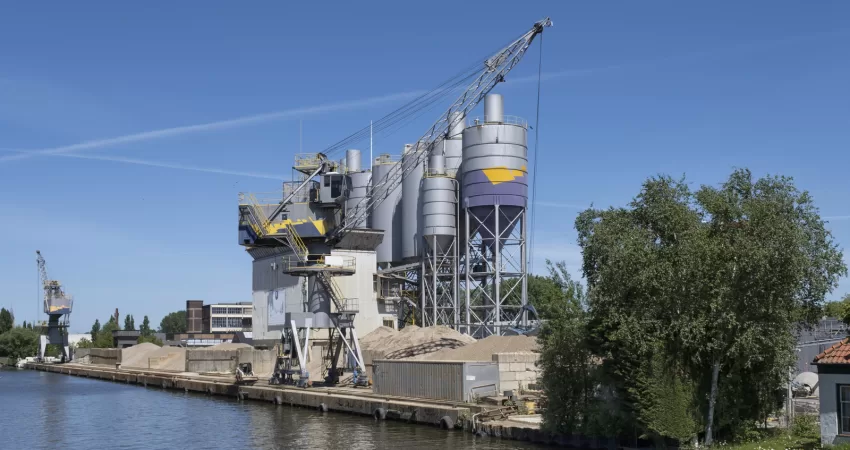
Bulk material handling design & system are used in many industries to efficiently store and transport heavy, loose, and bulky materials. These systems provide a safe, reliable, and cost-effective way to move large quantities of materials in a short period of time. Bulk material handling systems can be used for mining, construction, packaging, food processing, manufacturing, and other industries.
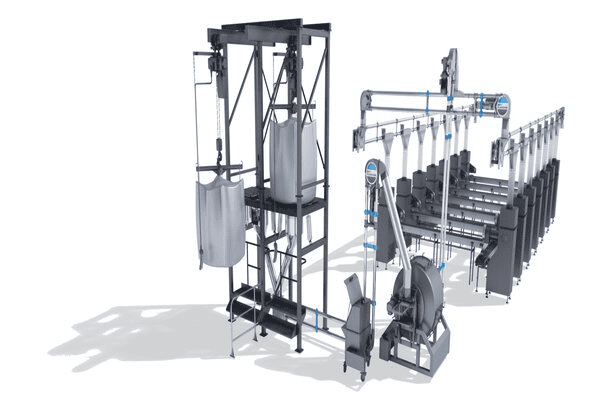
The design of bulk material handling systems has to consider the unique requirements of each application. The system must be able to move the right type and quantity of bulk material without damage or injury. Factors such as size, weight capacity, handling time requirements, safety features, cost-effectiveness and reliability must all be taken into account when designing the system. In addition to these factors there are also other important considerations such as environmental regulations that will further dictate the design choices that need to be made when creating a new system or upgrading an existing one
Types of Bulk Material Handling Systems
Depending on different industries, the type of Bulk Material Handling System varies. There are several types of Bulk Material Handling Systems that are distinguished according to their configuration, product characteristics and system capabilities. Below are the most common types of Bulk Material Handling Systems:
1. Conveyor Belt System: This is the most widely used system to move bulk materials horizontally or on an incline at a controlled rate. A combination of two or more conveyors can be used to transfer bulk materials through a plant efficiently and over long distances as well. A conveyor system can be combined with other material handling equipment for efficient process flow.
2. Truck Unloading/Loading System: Truck unloading and loading systems refer mainly to a collection of equipment that is used to unload materials from trucks and load them on different conveyors or other material handling equipment along the production line. Equipment such as hoppers, dumpers, conveyors etc., are typically used in truck unloading systems. Such systems can be customized according to product characteristics and production requirements.
3. Blending/Mixing System: Mixing systems are usually combined conveying and feeding operations in order to mix bulk solids accurately, homogenously and uniformly with no segregation during processing or transfer operations in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals or chemicals etc., Blending systems use machinery like pneumatic blenders, tumblers etc.,
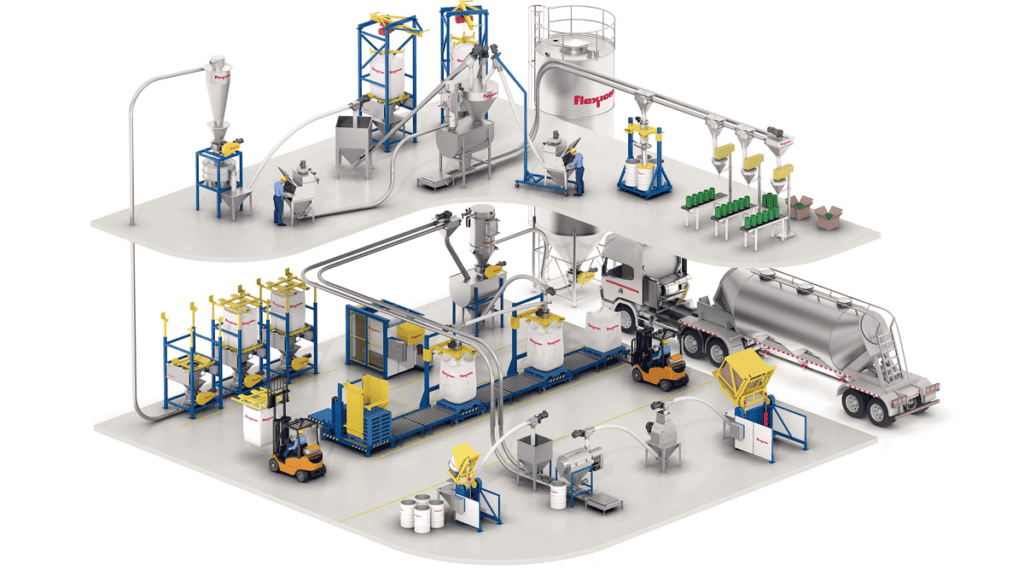
4. Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): AS/RS refers mainly to a computer-controlled operation containing automated storage-retrieval machines which operate within an enclosed structure like a warehouse where goods are automatically stored and retrieved without any operator intervention via computer interfaces for more efficient storage utilization compared to manual operations for large storage volumes
5 . Automated Palletizing System: An automated palletizing system is basically an end-of-line type robot system involving multiple robots managing multiple pallets simultaneously at high speeds without operator intervention in continuous production lines for better efficiency compared manual processes as it results in time savings with virtually no errors made compared manual operations
Factors to Consider During Design
There are several factors that must be considered in order to design an effective bulk material handling system. These include the type of material, flows, capacities, distances, environmental considerations, operator safety and ergonomics. It is important for designers to take into account all these characteristics when creating the system.
The type and size of material being handled play an important role in the design of a bulk material handling design and system as these impact flows, capacities and other factors that must be taken into consideration. The desired flow rate or capacity will determine much of the rest of the design features including required conveyor speeds and power ratings, as well as drive configurations.
Another factor to consider during design is the environment in which the system needs to run. Where will it be located? Which weather conditions will it need to operate effectively under? Will there be any extremes in temperatures or moisture levels? All these questions should be considered in order to ensure successful operation over time.
Operator safety and ergonomics are key elements that must also be addressed during a bulk material handling system’s design phase. Considerations such as guard railing height, emergency shut off systems, railings on access points and ladders should all be taken into account to ensure maximum operator safety at all times. Additionally, certain aspects like belt tracking can help improve operator comfort for longer periods of operation at any one time.
a. Cost
When considering the cost of a bulk material handling system, one should take into account the initial capital investment and installation costs as well as ongoing maintenance and replacement costs. It is important to factor in all relevant expenses when designing a system to ensure that it can be operated within budget. Depending on the material being handled, some parts of the bulk handling system may require more frequent replacement, thus driving up operating costs. Additionally, any automation elements should be carefully weighed as they often require larger up-front investments but can pay off in increased efficiency and productivity over time. It is essential to consider not just the upfront cost, but also what will be required for proper operation in order to make an informed decision about the best approach.
b. Capacity
Capacity is one of the most important factors to consider when designing a material handling system. It creates the basis for dimensioning and ensures that a sufficient flow-rate is available to satisfy operational needs. It also has an impact on the size and complexity of components in a material handling system, and ultimately affects the cost of purchase, operation and maintenance.
The capacity should be determined after assessing various parameters such as the materials’ physical properties, total quantity and necessary frequency of supply movement into storage or onto production areas. The appropriate dimensions must also be defined in order to ensure that maximum efficiency is achieved by all elements within the material handling system, especially if variable load factors are possible.
It’s important to have adequate reserve capacity as additional requirements may arise over time due to extended production runs or changes in throughput. Reserve capacity should also be factored into plans in order to cope with malfunctions or plant maintenance tasks which could lead to temporary overloading situations. Every planned alteration should always consider potential usage peaks lasting several hours or days before modifications are made.
c. Safety
The safety of personnel and equipment is paramount in designing a Bulk Material Handling System. Conveyors move large quantities of raw materials, high volumes of feedstock, aggressive chemicals and sometimes even people in manufacturing and industrial sites. Operating safely means protecting the organization from potential liability due to injury, property damage or pollution due to an incident with its equipment.
There are regulatory standards that govern the design and operation of bulk material handling systems in most countries. These are limits intended to avoid accidents, such as belt speed limits or maximum length travelled by a trolley on an overhead track before it stops at a station, with prescribed safety mechanisms applied when these parameters are exceeded. Hazardous locations may require specific design elements such as explosion-proof motors. Similarly, formal worker safety risk assessments must be carried out prior to any installation or operational start-up to ensure that all personnel have been adequately trained in equipment safety procedures.
Beyond regulations, proactive measures should also be undertaken by the organization such as machine guarding for rotating shafts and pulleys or proper distances for pedestrian walkways around moving conveyors etc., along with Warning signs at points of danger e.g blocking hazards like pinch points or hazardous substances being used for lubrication. This list can extend further depending upon the particular application but these are typical steps included in most material handling system designs..
d. Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of bulk materials handling systems must be taken into consideration to ensure a sustainable, safe and efficient system. Before designing a system, it is important to understand the potential risks posed by bulk material handling processes. Potential sources of pollution include air emissions, fugitive dust, water discharge, runoff and noise. Every effort should be taken to mitigate the environmental impacts associated with bulk material handling processes.
Air emissions in particular can potentially cause serious health issues for people working in or living near the area where bulk materials are handled. Proper planning will minimize significant environmental impacts from operations such as fugitive dust which can result from plant site and equipment operation when not properly managed and contained. Noise pollution while operating plant equipment also needs to be addressed as an issue posed by Bulk Material Handling Systems as it could have adverse effects on workers’ health and well-being as well as any nearby residential areas and wildlife.
Water discharge resulting from various operations such as handling waste materials requires careful management during design procedures that consider best management practices for preventing pollutants from entering bodies of water or groundwater sources. Moreover, runoff must also be addressed since uncontrolled runoff can pollute natural water sources, leading to habitat destruction and ecosystem degradation.
e. Maintenance Requirements
When designing a Bulk Material Handling System, it is important to consider the amount of maintenance required. Maintenance requirements can vary greatly depending on the materials being handled and the environment they are used in. It is essential to install an appropriate maintenance plan from the start, so that systems remain reliable and efficient.
Maintenance activities should include regular inspections, preventive measures such as lubrication/ greasing or other consumables, and adjustments as necessary. Careful records should be kept to monitor performance and track previously completed maintenance tasks. Further considerations for maintenance include:
– Selecting appropriate material of construction for components that are subject to wear
– Scheduling preventive maintenance with sufficient time between operations
– Training personnel on using safe work practices when conducting inspections
– Selecting various tools for inspecting components such as tightness testers, torque wrenches and more
– Utilizing safety guards if needed
Benefits of Bulk Material Handling Systems
Bulk material handling systems offer various efficient and cost-effective solutions for a wide range of materials, such as supplying fuels or raw materials to industrial plants, construction sites, shipping yards or mines. These systems are designed to be fully integrated with existing application and processes. Bulk material handling can guarantee consistent management of production lines and safe operation for personnel in hazardous areas.
The benefits of using bulk material handling systems include:
-Increased efficiency: Bulk material handling systems can help move high volumes of materials quickly, safely and reliably, leading to an improved working pace and minimised labour costs.
-Reduced material damage: By using a bulk material handling system, it reduces the risk of incidents that lead to product failure or inaccuracy during delivery.
-Improved safety: Automated systems can reduce manual intervention during the transfer process; this helps keep employees safe from hazardous working conditions or dangerous machines.
-Reduced costs: Bulk material handling offers increased cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods as they require decreased energy consumption and fewer resources are used throughout the handling process.
-Increased accuracy: By automating the entire transfer process bulk material handlers ensure precise measurement in terms of flow rate and precise weight readings which reduces potential errors from manual input data.
Challenges in Designing Bulk Material Handling Systems
Designing a bulk material-handling system involves more than just understanding the requirements of the materials being handled. The design process must also account for a variety of environmental and safety-related issues, as well as operational needs. Understanding the physical characteristics of the material and its anticipated handling requirements is crucial in developing a system that is both safe and efficient.
When designing a bulk material handling system, there are many factors to consider. The main considerations include:
1. Material Capacity: This refers to the total amount of material that can be moved through the system at any given time. This will dictate the size and shape of components needed to store and move materials, such as conveyors, hoppers and bins. Account must be taken for any changes in density or size due to settling or compaction over time.
2. Material Characteristics: This refers to any specific characteristics about the material itself, including particle size distribution, moisture content, temperature tolerance range, corrosivity and abrasiveness.
3. Environmental Safety: The design should take into account potential environmental risks associated with operation of the system in areas such as air quality control and noise pollution prevention initiatives (such as use of sound barriers).
4. Product Integrity & Quality Control: The design should create minimal physical disturbance during transport (such as segregation) while still allowing product adhering to industry quality standards can minimize customer complaints or insurer claims later on down the line
5. Occupational Health & Safety: Design features should include safeguards to protect operators from risks related to working in close proximity with potentially hazardous materials (such as dust collection systems). Likewise; access points throughout various stages must be positioned so that workers can carry out inspections where necessary without compromising safety standards or productivity rates
6 Operational Performance: Key performance indicators such as efficiency, cycle times throughput capacity; set up/changeover times; load/unload rates etc., should be taken into account when designing systems capable not only for optimum performance but maximum flexibility when responding rapidly changing market demands .
Best Practices for Bulk Material Handling System Design
The design of a bulk material handling system requires careful consideration of a wide variety of potential variables. To ensure the successful creation, installation and use of your system, it is important to consider factors such as the equipment being used for transportation and unloading, the relevant safety considerations for personnel in and around the system, as well as environmental constraints such as dust control or spills.
Best practices for bulk material handling systems design are based on application requirements combined with a thorough exploration of available solutions. Factors to consider include:
-Requirements analysis: This includes researching relevant regulations and industry standards, as well as specific customer requirements or preferences.
-Product characterization: Examining the physical properties such as size, shape, weight and abrasiveness will help inform decisions related to how the product should be handled.
-Selection criteria: Along with factors like cost performance ratio for initial investments and longevity; other factors like overall reliability, flexibility in system capacities and scalability over varying volumes should also be considered.
-Industry expertise: Having an experienced team that understands industry best practices can provide insight into efficient solutions combined with safe operations that minimize downtime while maximizing throughput capacity.
Once these best practices have been considered during the design process, continual evaluations should also be conducted to ensure optimal performance over time by evaluating components like safety features or production levels relating to key metrics such as profitability.
Conclusion
The success of any bulk material handling system will depend on its design. To ensure the longevity of the system, designers should take into account local laws and regulations, potential hazards, required throughput levels, efficient storage layouts and other possible factors that could affect its efficiency. Additionally, these systems should be designed to meet their intended objectives while taking into account available resources with a communication network throughout the equipment so that any improvements can be made swiftly. With the right design considerations in place, bulk material handling systems can ensure efficient operation while minimizing risks and costs.
References
When designing a Bulk Material Handling System, it is important to consult several reference sources to ensure the most appropriate system is chosen. These can include books, videos, articles and people who are experienced in the industry.
Books such as ‘Bulk Material Handling Systems Design’ can provide an excellent foundation for gaining knowledge about system design and construction. There are also several discipline-specific texts available to cover topics such as safety and logistics.
Videos are another useful source of information for bulk material handling systems. Many online sites offer tutorials or demonstrations on different aspects of system design or construction, while video courses may be found in textbooks or taken as part of a college course. The benefit of this media is that you’ll have the chance to actually see the equipment being used before you construct your own system.
Articles discussing bulk material handling systems can often provide valuable insight into the subject matter at hand. Many trade magazines are devoted solely to the topic and contain up-to-date advice concerning its design and operation. In addition, online searches will generally yield a wealth of references compiled by industry experts that could prove invaluable when planning a project.
Finally, speaking with people who have experience using or constructing bulk material handling systems can provide an irreplaceable source of information when developing one’s own project plans. A professional engineer usually provides invaluable guidance regarding complex components and other issues that may arise during the design process; even seeking counsel from colleagues in the same business sector can often result in sound advice that could save both time and money during installation and operation afterwards.
